News
Central Black Hole Detections Jump near Milky Way Mass
Posted January 8, 2025
RESOLVE/ECO team research to be published in the Astrophysical Journal reveals that active galactic nuclei (AGN, or growing massive black holes) are roughly five times more common in mid-size galaxies like the Milky Way than in dwarf galaxies. Using multiple optical and mid-infrared techniques to cut through the glare of star formation, we found AGN in 2-5% of dwarf galaxies, exceeding most prior estimates. Nonetheless, AGN jumped sharply to 16-27% in the transitional mass range between dwarfs and giants, which includes the Milky Way at its upper end. The abstract of our submitted and favorably refereed paper is below, and you can follow the two links below to check out the American Astronomical Society meeting
• i-poster (available as of 1/7/2026) and
• press conference (live 1/8/2026 2:15pm MST + recorded)
regarding this work.
This research was part of Dr. Mugdha Polimera's PhD dissertation in the UNC Physics & Astronomy Department, completed with Prof. Sheila Kannappan and the RESOLVE/ECO survey team. Dr. Polimera now works for the NASA ADS (Astrophysics Data System) at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard and Smithsonian, which has also issued a news release.
A Comprehensive AGN Inventory for the Dwarf-Dominated RESOLVE and ECO Surveys: Mass-Dependent AGN Types and Occupation Fractions
Polimera, Mugdha S., Kannappan, Sheila J., Richardson, Chris T., Stark, David V., Eckert, Kathleen D., Jarrett, Thomas H., Carr, Derrick S., Hutchens, Zackary L., Bellovary, Jillian M., and Norris, Mark A.
We catalog Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) in the volume- and mass-limited RESOLVE and ECO surveys using (i) the BPT plot with standard and alternate demarcations, (ii) the BPT plot and VO plots (using [OI] or [SII]) to find "SF-AGN" with mixed star-forming and AGN classifications, and (iii) mid-IR WISE color selection. Dividing RESOLVE+ECO into dwarf, transitional, and giant galaxies by baryonic mass, we find AGN occupation fractions of 2-5%, 16-27%, and 20-48%, respectively, computed relative to all galaxies in each mass range including those not searchable for AGN. These percentage ranges encompass large systematics between crossmatched emission-line measurements from different SDSS catalogs. Stellar-mass divisions yield similar results. Adding (incomplete) archival X-ray/broadline AGN detections, the dwarf AGN occupation fraction reaches 3-6. WISE AGN are detected in <1% of galaxies at all masses with optimized WISE photometry; we show that standard catalog photometry yields high rates of both false positives and false negatives. AGN demographics shift with mass due to correlations with gas content, star formation, and group environment, forming a continuum: SF-AGN at the high-SF end, then "Bonus AGN" (defined by alternate literature BPT demarcations), then Composites, then Conventional AGN at the low-SF end. Typical (metal-poor, star-forming) dwarfs most often host SF-AGN, whereas typical transitional galaxies most often host Bonus AGN and Composites. We release homogenized SDSS line measurements, reprocessed WISE data, and UV+mid-IR star formation rates for RESOLVE and ECO.
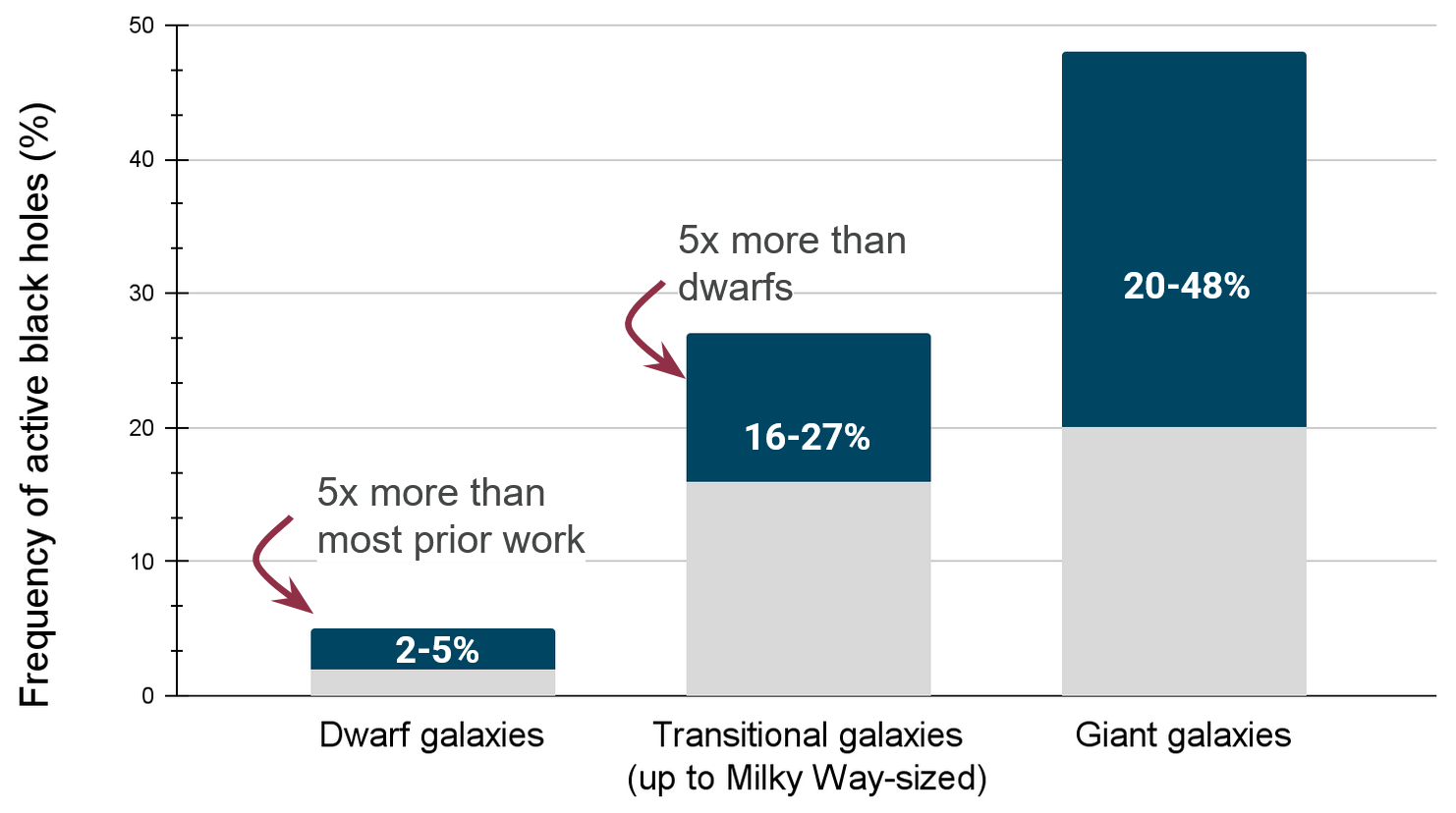 Though our optimized techniques find roughly five times more active black holes in dwarf galaxies than most prior work does, we emphasize that the 2-5% frequency measured for dwarfs is still far lower than the 16-27% frequency for transitional galaxies -- galaxies with masses between dwarfs and giants, like our own Milky Way -- or the 20-48% frequency for giants. This bar chart uses two shades to show these very broad percentage ranges, which are so approximate because of large systematic differences between emission-line measurements by different research teams using the same SDSS spectroscopic data. Even so, we found an unmistakable jump in the measured frequency of active black holes going from dwarfs to transitional and giant galaxies, which could mean that there are still more black holes eluding detection in dwarfs, or could mean that as they transition from dwarfs to giants, galaxies become better places for black holes to grow.
Though our optimized techniques find roughly five times more active black holes in dwarf galaxies than most prior work does, we emphasize that the 2-5% frequency measured for dwarfs is still far lower than the 16-27% frequency for transitional galaxies -- galaxies with masses between dwarfs and giants, like our own Milky Way -- or the 20-48% frequency for giants. This bar chart uses two shades to show these very broad percentage ranges, which are so approximate because of large systematic differences between emission-line measurements by different research teams using the same SDSS spectroscopic data. Even so, we found an unmistakable jump in the measured frequency of active black holes going from dwarfs to transitional and giant galaxies, which could mean that there are still more black holes eluding detection in dwarfs, or could mean that as they transition from dwarfs to giants, galaxies become better places for black holes to grow.